Skill builder topic 4.3 rates of change in applied contexts – Skill Builder Topic 4.3: Rates of Change in Applied Contexts delves into the practical applications of rates of change, exploring how they are utilized across diverse fields to solve real-world problems and make informed decisions.
This topic will examine the various methods for calculating rates of change, including the average rate of change, the instantaneous rate of change, and the slope of a line. We will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each method and explore how rates of change are applied in finance, physics, engineering, and other disciplines.
Rates of Change in Applied Contexts

Rates of change measure how a quantity changes over time. They are used in various fields to understand and predict changes in real-world phenomena.
Definition of Rates of Change in Applied Contexts
In applied contexts, rates of change describe how a variable or quantity varies with respect to another variable, usually time. They quantify the change in a dependent variable as the independent variable changes.
Rates of change provide valuable insights into the dynamics of systems and processes. They help predict future behavior, optimize operations, and make informed decisions.
Methods for Calculating Rates of Change, Skill builder topic 4.3 rates of change in applied contexts
There are several methods for calculating rates of change, depending on the nature of the data and the desired level of precision.
- Average Rate of Change:The average rate of change measures the change in a quantity over a specified interval. It is calculated by dividing the change in the quantity by the change in the independent variable.
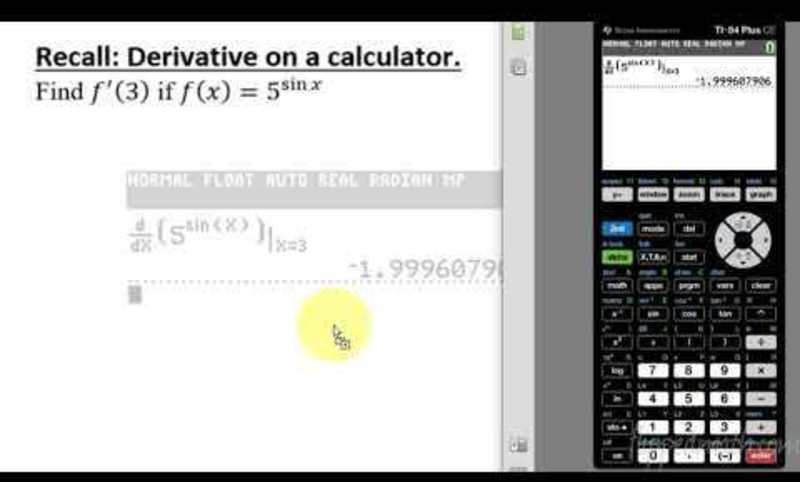
- Instantaneous Rate of Change:The instantaneous rate of change measures the rate of change at a specific point in time. It is calculated using the derivative of the function that describes the quantity’s change.
- Slope of a Line:The slope of a line is a measure of the rate of change of a linear function. It is calculated by dividing the change in the dependent variable by the change in the independent variable.
Applications of Rates of Change in Different Fields
Rates of change have wide-ranging applications across various fields, including:
- Finance:Calculating interest rates, stock prices, and investment returns.
- Physics:Determining velocity, acceleration, and the rate of radioactive decay.
- Engineering:Designing bridges, buildings, and other structures to withstand changes in load and environmental conditions.
Case Studies and Examples
Real-world case studies and examples demonstrate how rates of change are used to solve problems and make decisions:
- Predicting Population Growth:Rates of change are used to model population growth and forecast future population size, which is crucial for urban planning and resource allocation.
- Optimizing Production Processes:Manufacturers use rates of change to monitor production lines and identify bottlenecks, enabling them to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Analyzing Stock Market Trends:Investors use rates of change to identify trends in stock prices and make informed investment decisions.
Limitations and Considerations
When using rates of change in applied contexts, it is important to consider their limitations:
- Assumptions:Rates of change assume that the relationship between the variables is linear or follows a known function.
- Data Accuracy:The accuracy of the calculated rates of change depends on the accuracy of the underlying data.
- Time Scale:The time scale over which the rates of change are calculated can affect the results.
FAQ Overview: Skill Builder Topic 4.3 Rates Of Change In Applied Contexts
What is the definition of rate of change?
Rate of change refers to the measure of how a quantity changes over time or with respect to another variable.
How is the average rate of change calculated?
The average rate of change is calculated by dividing the change in the dependent variable by the change in the independent variable over a given interval.
What is the difference between the average rate of change and the instantaneous rate of change?
The average rate of change measures the change over an interval, while the instantaneous rate of change measures the change at a specific point in time.