Two types of evacuation methods used by technicians are a cornerstone of emergency response, providing a structured approach to ensuring the safety of individuals during critical situations. These methods, horizontal and vertical evacuation, each possess distinct advantages and disadvantages, necessitating careful consideration when selecting the most appropriate technique for a given scenario.
Horizontal evacuation involves the movement of individuals to a safer location within the same level of a building or structure, typically away from the source of danger. This method is often employed in situations where vertical evacuation is not feasible or poses significant risks, such as during fires or chemical spills.
Conversely, vertical evacuation entails the movement of individuals to a higher or lower level of a building or structure, often utilizing stairs or elevators. This method is commonly used in situations where horizontal evacuation is not possible, such as during earthquakes or floods.
Types of Evacuation Methods
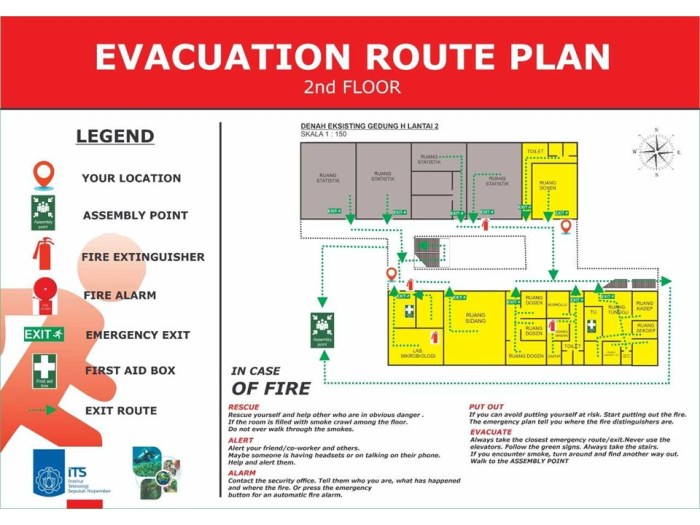
Evacuation methods are essential for ensuring the safety of individuals during emergencies. Technicians utilize two primary types of evacuation methods: horizontal evacuation and vertical evacuation.
Horizontal Evacuation
Horizontal evacuation involves moving individuals away from a hazard on the same level. This method is typically used when the hazard is contained to a specific area and does not pose an immediate threat to life or property. Examples of horizontal evacuation include:
- Evacuating a building during a fire
- Relocating people away from a chemical spill
- Moving individuals out of a flood zone
Vertical Evacuation, Two types of evacuation methods used by technicians are
Vertical evacuation involves moving individuals to a higher level to escape a hazard. This method is typically used when the hazard is widespread or poses an immediate threat to life or property. Examples of vertical evacuation include:
- Evacuating a building during an earthquake
- Moving people to a rooftop during a flood
- Escaping a fire by climbing to a higher floor
Factors Influencing Evacuation Method Selection
The choice of evacuation method depends on several factors, including:
- The nature of the hazard
- The severity of the hazard
- The location of the hazard
- The number of people to be evacuated
- The availability of resources
Technicians must carefully assess the situation and determine the most appropriate evacuation method based on these factors.
Equipment and Resources for Evacuation: Two Types Of Evacuation Methods Used By Technicians Are
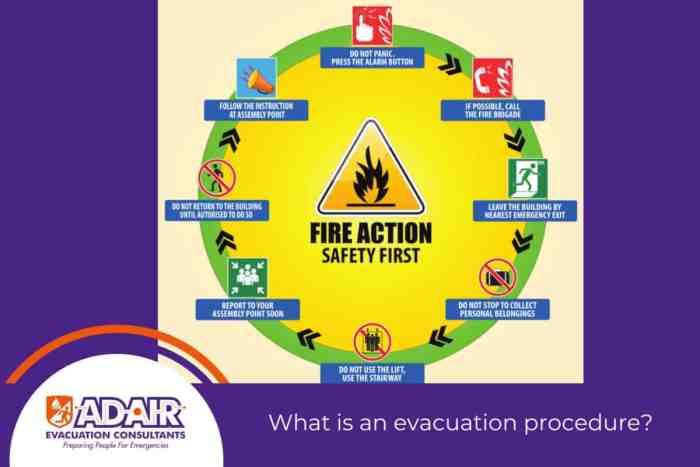
| Equipment | Horizontal Evacuation | Vertical Evacuation | Common to Both |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flashlights | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| First-aid kits | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Stretchers | Yes | No | Yes |
| Ladders | No | Yes | Yes |
| Ropes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Gas masks | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Radios | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Training and Certification for Evacuation Technicians

Evacuation technicians must undergo specialized training and certification to ensure they possess the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively perform their duties. This training typically includes:
- Emergency planning and response
- Evacuation procedures
- First aid and CPR
- Hazard recognition and assessment
- Equipment and resource management
Proper training and certification are essential to ensure the safety and effectiveness of evacuation operations.
FAQ Compilation
What are the key differences between horizontal and vertical evacuation?
Horizontal evacuation involves moving individuals to a safer location on the same level, while vertical evacuation involves moving individuals to a higher or lower level.
When is horizontal evacuation typically used?
Horizontal evacuation is often used when vertical evacuation is not feasible or poses significant risks, such as during fires or chemical spills.
What factors influence the choice of evacuation method?
Factors that influence the choice of evacuation method include the nature of the hazard, the condition of the building or structure, and the capabilities of the individuals involved.