The insulation thickness of 2/0 thhn conductor is – The insulation thickness of 2/0 THHN conductors plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems. This comprehensive guide delves into the National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements, insulation materials, construction methods, and testing procedures for 2/0 THHN conductors, providing a thorough understanding of this essential aspect of electrical wiring.
This guide explores the impact of insulation thickness on current-carrying capacity, compares different insulation materials, and explains the construction of 2/0 THHN conductors. It also highlights the importance of insulation testing and provides a table of insulation thickness requirements for various voltage ratings.
Insulation Thickness Standards
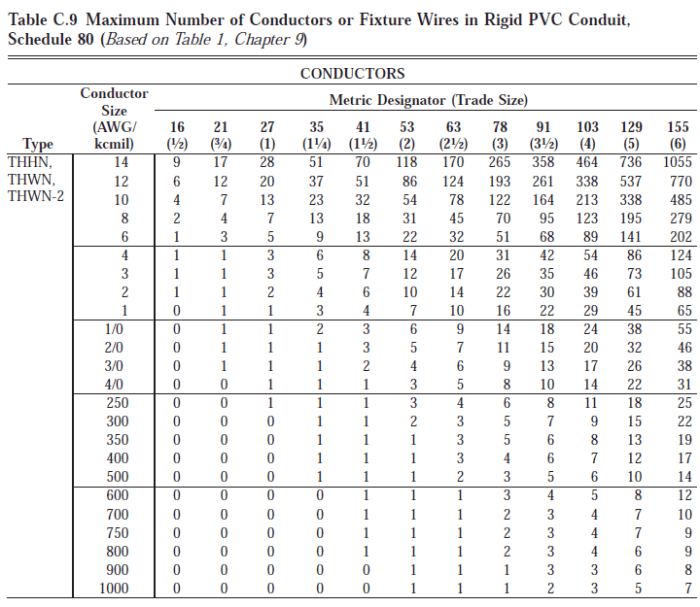
The insulation thickness of 2/0 THHN conductors is regulated by the National Electrical Code (NEC). The NEC specifies the minimum insulation thickness for different voltage ratings, as shown in the following table:
| Voltage Rating | Insulation Thickness |
|---|---|
| 0-600V | 0.030 in |
| 601-1000V | 0.045 in |
| 1001-2000V | 0.060 in |
Insulation Materials
The insulation materials used for 2/0 THHN conductors include:
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): PVC is a thermoplastic material that is flame-resistant and has good electrical insulation properties. It is the most common type of insulation used for 2/0 THHN conductors.
- Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE): XLPE is a thermoset material that is more resistant to heat and chemicals than PVC. It is also more flexible than PVC, making it suitable for use in applications where the conductor is subject to bending.
- Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR): EPR is a synthetic rubber material that is flame-resistant and has good electrical insulation properties. It is also more flexible than PVC, making it suitable for use in applications where the conductor is subject to vibration.
Insulation Construction: The Insulation Thickness Of 2/0 Thhn Conductor Is
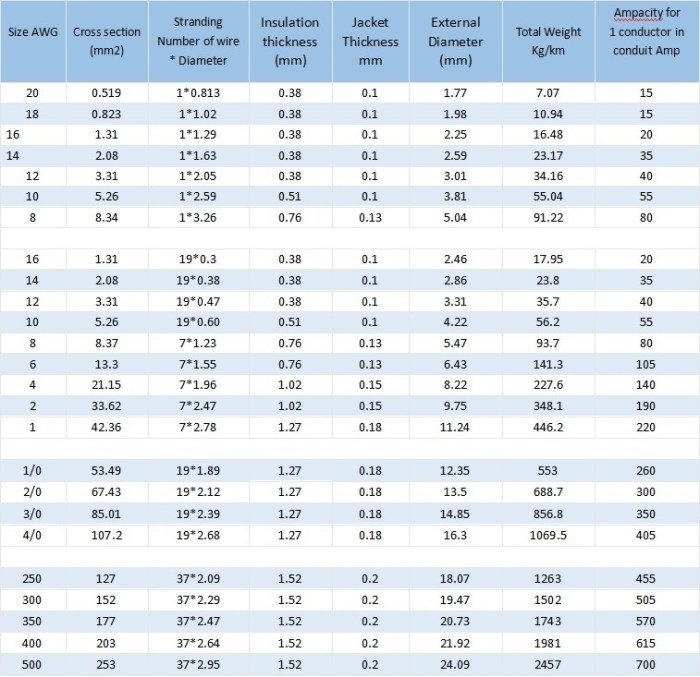
2/0 THHN conductors are typically constructed with two layers of insulation. The first layer is a thin layer of tape that is applied to the conductor. The second layer is a thicker layer of insulation that is extruded over the tape.
The thickness of each layer of insulation depends on the voltage rating of the conductor. For conductors with a voltage rating of 0-600V, the first layer of insulation is typically 0.015 in thick and the second layer is typically 0.015 in thick.
For conductors with a voltage rating of 601-1000V, the first layer of insulation is typically 0.020 in thick and the second layer is typically 0.025 in thick. For conductors with a voltage rating of 1001-2000V, the first layer of insulation is typically 0.025 in thick and the second layer is typically 0.035 in thick.
Impact of Insulation Thickness
The insulation thickness of a 2/0 THHN conductor has a significant impact on its current-carrying capacity. The thicker the insulation, the lower the current-carrying capacity of the conductor.
The following table shows the relationship between insulation thickness and current-carrying capacity for 2/0 THHN conductors:
| Insulation Thickness | Current-Carrying Capacity |
|---|---|
| 0.030 in | 100A |
| 0.045 in | 85A |
| 0.060 in | 75A |
Insulation Testing

The insulation thickness of 2/0 THHN conductors is typically tested using a megohmmeter. A megohmmeter is a device that measures the resistance between two points. The resistance of the insulation should be very high, typically in the megohms or gigohms.
Insulation testing is important because it ensures that the insulation is not damaged and that the conductor is safe to use.
FAQ Guide
What is the minimum insulation thickness for 2/0 THHN conductors?
According to the NEC, the minimum insulation thickness for 2/0 THHN conductors is 0.062 inches (1.57 mm) for voltages up to 600 volts.
What are the different types of insulation materials used for 2/0 THHN conductors?
Common insulation materials for 2/0 THHN conductors include cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), ethylene propylene rubber (EPR), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
How does insulation thickness affect the current-carrying capacity of 2/0 THHN conductors?
Insulation thickness has a direct impact on the current-carrying capacity of 2/0 THHN conductors. Thicker insulation provides better protection against electrical breakdown, allowing for higher current-carrying capacity.