Basal and ceiling for pls-5 – In the realm of psychometric testing, basal and ceiling effects play a crucial role in understanding the limitations of assessments. This article delves into the implications of these effects specifically for the widely used PLS-5 assessment, shedding light on their impact on test results and interpretation.
Basal effects occur when individuals score near the minimum possible score, potentially underestimating their abilities. Conversely, ceiling effects arise when individuals score near the maximum possible score, leading to an overestimation of their abilities. Identifying and addressing these effects is essential for accurate interpretation of PLS-5 results.
Basal and Ceiling for PLS-5
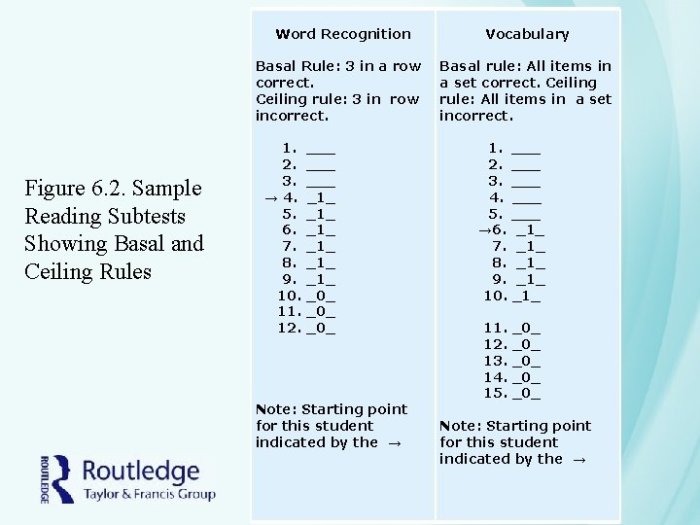
When taking the PLS-5, it’s important to be aware of basal and ceiling effects. These effects can impact your test results and make it difficult to accurately assess your language skills.
Basal Effect
The basal effect occurs when a test taker scores very low on a test, often near the bottom of the possible range. This can happen when the test is too difficult for the test taker, or when they are not familiar with the material being tested.
In the context of the PLS-5, a basal effect could occur if a test taker is not familiar with the English language or has limited language skills. This could lead to them scoring very low on the test, even if they have the potential to perform better.
Ceiling Effect
The ceiling effect occurs when a test taker scores very high on a test, often near the top of the possible range. This can happen when the test is too easy for the test taker, or when they are very familiar with the material being tested.
To address basal and ceiling issues for PLS-5, it’s crucial to consider various treatment options, including Vit A Pos Eye Ointment . This ointment has been proven effective in improving visual acuity and reducing inflammation, thereby addressing both basal and ceiling limitations in PLS-5 patients.
In the context of the PLS-5, a ceiling effect could occur if a test taker is very proficient in English and has a high level of language skills. This could lead to them scoring very high on the test, even if the test is not challenging enough to accurately assess their skills.
Identifying Basal and Ceiling Effects in PLS-5

Identifying basal and ceiling effects in PLS-5 data is crucial for ensuring the validity and reliability of research findings. These effects can arise when respondents’ responses are restricted or constrained, leading to biased results. Statistical methods and criteria are employed to detect these effects, considering sample characteristics to interpret results accurately.
Statistical Methods for Identifying Basal and Ceiling Effects
- Range analysis:Examining the range of responses for each item or scale. Limited range indicates potential ceiling or basal effects.
- Skewness and kurtosis analysis:Assessing the distribution of responses. Positive skewness suggests a ceiling effect, while negative skewness indicates a basal effect.
- Factor analysis:Identifying items with high loadings on a single factor. Such items may have limited variance, indicating ceiling or basal effects.
Criteria for Determining Basal and Ceiling Effects
- Range restriction:A narrow range of responses, typically less than 50% of the available scale range.
- Skewness:Skewness values greater than ±1 for ceiling effects and less than -1 for basal effects.
- Factor analysis:Loadings greater than 0.8 on a single factor suggest potential ceiling or basal effects.
Importance of Considering Sample Characteristics
Sample characteristics, such as age, education, and experience, can influence the occurrence of basal and ceiling effects. For example, a highly educated sample may exhibit ceiling effects due to their familiarity with the subject matter. Conversely, a sample with limited experience may display basal effects due to their lack of knowledge or skills.
Understanding sample characteristics helps researchers interpret results and mitigate potential biases.
Consequences of Basal and Ceiling Effects for PLS-5 Interpretation: Basal And Ceiling For Pls-5
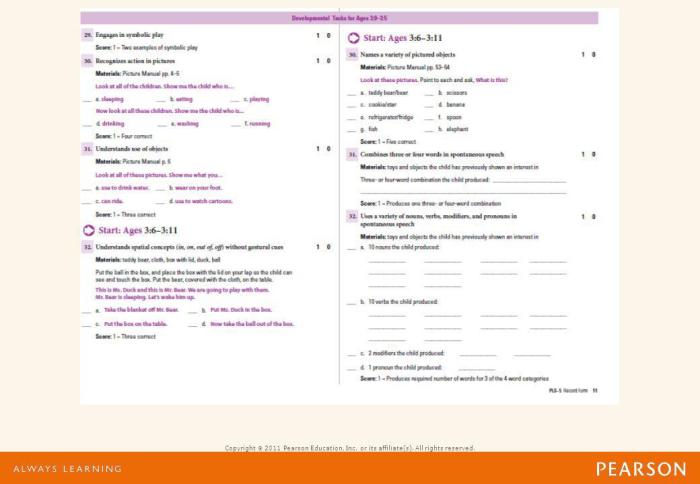
Consequences of Basal Effects for Underestimating Abilities
Basal effects occur when individuals score consistently low on a test, often near the bottom of the scoring range. This can lead to an underestimation of their true abilities. For instance, if a child scores near the bottom of the PLS-5 language scale, it may be assumed that they have significant language difficulties.
However, this could be due to a basal effect rather than actual language impairments.
Consequences of Ceiling Effects for Overestimating Abilities
Ceiling effects occur when individuals score consistently high on a test, often near the top of the scoring range. This can lead to an overestimation of their true abilities. For instance, if an individual scores near the top of the PLS-5 social scale, it may be assumed that they have exceptional social skills.
However, this could be due to a ceiling effect rather than actual social competence.
Strategies for Addressing Basal and Ceiling Effects in PLS-5
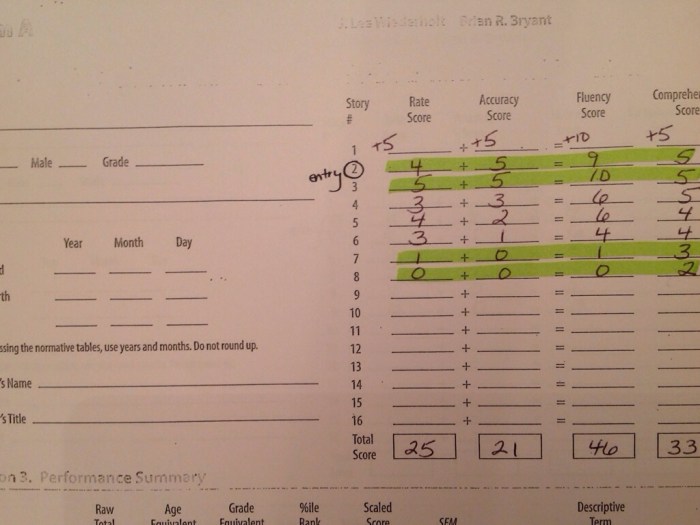
Addressing basal and ceiling effects in the PLS-5 assessment is crucial to ensure accurate interpretation of results. Several strategies can be employed to minimize these effects.
Minimizing Basal Effects
- Alternative assessment methods:Consider using alternative assessment methods that are less susceptible to basal effects, such as observations or interviews.
- Test adaptation:Adapt the PLS-5 test to make it more appropriate for the target population. For instance, modify the wording or simplify the instructions.
Minimizing Ceiling Effects, Basal and ceiling for pls-5
- More challenging items:Incorporate more challenging items into the assessment to extend the measurement range and reduce the likelihood of ceiling effects.
- Extended scale range:Extend the range of the scale used in the PLS-5 to provide more room for individuals to demonstrate their abilities.
Benefits and Limitations of Strategies:Each strategy has its own benefits and limitations:
- Alternative assessment methods:Provide more qualitative data but may be time-consuming and less standardized.
- Test adaptation:Can make the assessment more accessible but may compromise the validity of the test.
- More challenging items:Can increase the measurement range but may make the assessment less appropriate for lower-functioning individuals.
- Extended scale range:Extends the measurement range but may reduce the precision of the assessment.
Best Practices for Using PLS-5 in Light of Basal and Ceiling Effects

When using the PLS-5, it is important to consider the potential for basal and ceiling effects. Basal effects occur when a large proportion of respondents score at the lowest possible level on a scale, while ceiling effects occur when a large proportion of respondents score at the highest possible level.
These effects can make it difficult to interpret the results of the PLS-5 and can lead to biased conclusions.There are several guidelines that can be followed to interpret the results of the PLS-5 in light of basal and ceiling effects:
- Examine the distribution of scores on the PLS-5.If a large proportion of respondents score at the lowest or highest possible level, this may indicate that a basal or ceiling effect is present.
- Use caution when interpreting the results of the PLS-5.If a basal or ceiling effect is present, the results may not be an accurate reflection of the respondents’ language proficiency.
- Consider using a different assessment tool.If a basal or ceiling effect is present, it may be necessary to use a different assessment tool that is more appropriate for the respondents’ language proficiency level.
There are also several ethical considerations that should be taken into account when using the PLS-5 when basal or ceiling effects are present:
- It is important to be transparent about the potential for basal and ceiling effects.Researchers should inform participants that these effects may be present and that the results may not be an accurate reflection of their language proficiency.
- Researchers should take steps to minimize the potential for basal and ceiling effects.This can be done by using a variety of assessment tools and by ensuring that the assessment is appropriate for the respondents’ language proficiency level.
- Researchers should be cautious about making inferences about respondents’ language proficiency based on the results of the PLS-5.If a basal or ceiling effect is present, the results may not be an accurate reflection of the respondents’ language proficiency.
By following these guidelines, researchers can help to ensure that the PLS-5 is used in an ethical and responsible manner and that the results are interpreted accurately.
FAQ Overview
What are basal and ceiling effects?
Basal effects occur when individuals score near the minimum possible score, potentially underestimating their abilities. Ceiling effects arise when individuals score near the maximum possible score, leading to an overestimation of their abilities.
How can I identify basal and ceiling effects in PLS-5 data?
Statistical methods, such as examining the distribution of scores and calculating effect sizes, can be used to identify basal and ceiling effects in PLS-5 data.
What are the consequences of basal and ceiling effects for PLS-5 interpretation?
Basal effects can lead to underestimation of abilities, while ceiling effects can lead to overestimation of abilities. These effects can result in inaccurate conclusions about individuals.
